UPS System: How It Works and Why It Matters
In today’s highly connected world, continuous electricity is essential. A UPS system plays a critical role in keeping important services running when power problems occur. From data centers to hospitals, reliable backup power ensures that operations remain safe, stable, and uninterrupted.
Why a UPS System Is Important
We rely on electricity for communication, business, healthcare, and transportation. However, power outages, voltage fluctuations, and electrical disturbances can happen at any time. As a result, even a short interruption may cause data loss, equipment damage, or costly downtime.
Therefore, installing a UPS system is one of the most effective ways to protect critical operations. In addition, modern power protection solutions are widely used in:
- Data centers and IT rooms
- Hospitals and medical facilities
- Office buildings and factories
- Telecom and network infrastructure
- Marine and transportation systems
In each of these environments, an uninterruptible power supply ensures continuous and high-quality electricity.
What Does a UPS System Do?
A UPS system is a backup power device that keeps equipment running during a power failure. Instead of relying only on the utility grid, it uses batteries to supply electricity instantly when a problem occurs.
The backup time depends on battery capacity and load requirements. Generally, the larger the battery bank, the longer the system can support the connected equipment.
For example, a UPS can:
- Keep life-saving medical equipment operating during outages
- Protect data centers from shutdown during storms or surges
- Maintain communication systems in ships or remote locations
Clearly, although often unnoticed, backup power systems are essential for modern life.
Power Protection and Power Quality
Besides providing emergency energy, a UPS system also improves power quality. In other words, it acts as a filter that protects equipment from:
- Voltage spikes and surges
- Frequency variations
- Electrical noise and interference
- Micro-interruptions
As a result, connected devices receive clean and stable sine-wave power. Consequently, equipment operates more reliably and enjoys a longer service life.
Key Components of a UPS System
To understand how a UPS works, it is important to know its main parts:
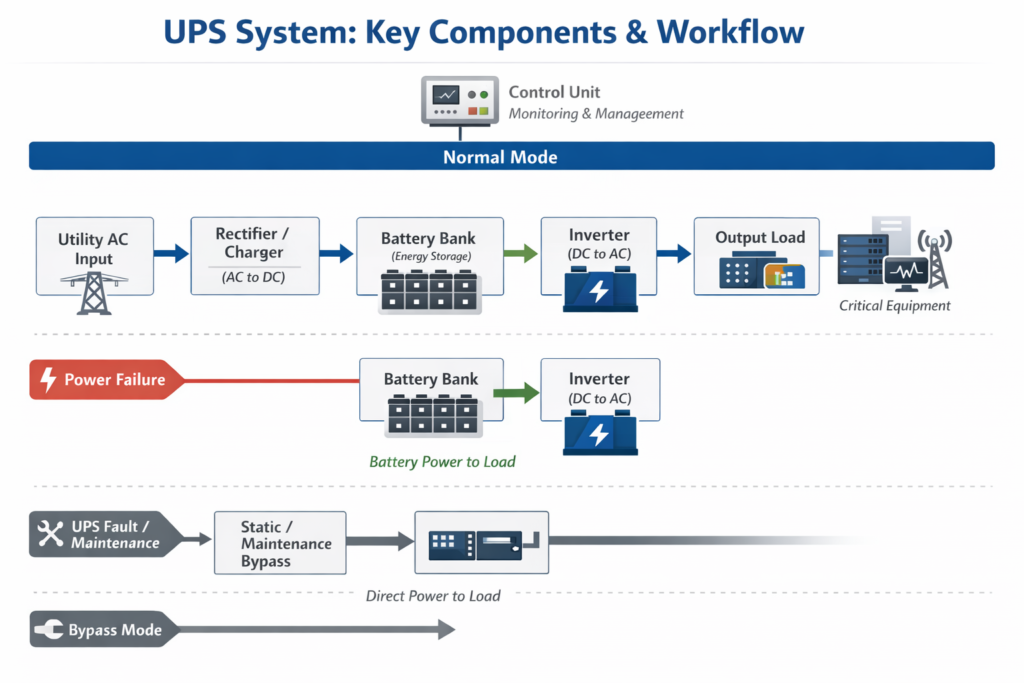
- Rectifier/Charger
Converts AC input power into DC to charge the batteries and supply the inverter.
2. Battery
Stores energy and provides backup power during outages.
3. Inverter
Converts DC power from the battery or rectifier back into AC for the load.
4. Static and Maintenance Bypass
Allows the load to be transferred directly to the utility if the UPS requires service or experiences a fault.
5. Control Unit
Monitors system performance and provides intelligent management, alarms, and communication functions.
Normal Operation
Under normal conditions, utility power enters the UPS system and passes through the rectifier. First, AC power is converted into DC. Then:
- Part of the energy charges the batteries
- The remaining power feeds the inverter
- Finally, the inverter supplies stable AC to connected equipment
This process ensures constant voltage and clean output power at all times.
What Happens During a Power Failure?
If the utility power fails or falls outside acceptable limits, the system responds immediately. At this moment, the inverter switches to battery power without interruption. Therefore, the load continues to operate smoothly and safely.
The backup duration depends on battery capacity and load demand. Once the main power returns to normal, the rectifier resumes operation and recharges the batteries automatically.
What If the UPS Needs Maintenance?
If a fault occurs or maintenance is required, the static bypass activates automatically. In this case, the load is transferred directly to the utility power source. As a result, electricity remains available even during service conditions.
Because of this design, a UPS system can maintain power continuity under almost any situation.
Smart Monitoring and Advanced Functions
Modern UPS solutions include intelligent controllers and software. These features provide:
- Real-time system monitoring
- Remote management
- Event recording and alarms
- Customized operating settings
Consequently, users can improve reliability, reduce risks, and plan maintenance more efficiently.
Summary
In summary, a UPS system is far more than a simple battery backup. It ensures continuous operation, protects sensitive equipment, and improves power quality. As businesses and infrastructure become more dependent on electricity, reliable backup power is no longer optional—it is essential.
Greenet’s UPS work for many countries and they are the best solution for your work and daily life, check more details of the products bellow:


